Technical Support
SOLCO are a leading specialist company, supplying high quality innovative compliant products for Structural Waterproofing, Gas Protection and specialist Building Chemical Solutions for the Building, Construction and Civil Engineering markets. We can provide cost effective design solutions for all types of specialist applications underwritten by qualified speciation engineers
Our
Product Support Services
Our
Product Support Services

Solco Gas Product Selector
Gas & Waterproof Product Selector |
Radon
|
Bulk Ground Gas to NHBC (Amber 1) |
Carbon Dioxide & Methane
|
Hydrocarbon / VOC
|
Hydrocarbon / VOC
|
Waterproof
|
Agrément Certificate |
| Solco TS Amber 1 Radon Membrane | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | ||||
| Solshield High Performance DPM | ✓ | BBA | |||||
| Solshield Reinforced Gas Barrier | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | ||||
| Solshield Ultra Gas Barrier | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | ||
| Solshield Flexible Hydrocarbon Barrier | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Solshield CT Bond Crystalline (NEW) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BDA (Applied) |
| Solshield CT Bond Pre (NEW) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BDA (Applied) |
| Solsheet Self-Adhesive Membrane | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | |||
| Solsheet GR Self-Adhesive Membrane | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | |
| Solseal Flexible Liquid Membrane | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Solseal Liquid Gas Barrier | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Solseal PB-2K | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Solcourse HP DPC | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | ||||
| Solcourse GR DPC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BBA | |||
| Solcourse 3S DPC | ✓ | BBA | |||||
| Actitex Bentonite Membrane | ✓ | BDA |
What is Gas Protection?
Note: BS8485:2015, Section 4
Protection from hazardous gases and other contaminants present in underlying soils, that can pose various risks to occupiers, and to the structures themselves if not managed. Gas protection measures are used to interrupt any possible gas ingress routes.
Protection measures should be:
- Durable
- Buildable
- Effective
- Robust
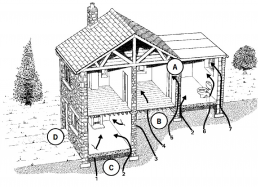
Key To Ingress Routes:
1. Through cracks in solid floors
2. Through construction joints
3. Through cracks in walls below ground level
4. Through gaps in suspended floors
5. Through cracks in walls
6. Through gaps around service pipes
7. Through cavities in walls
Key To Ingress Routes:
A. Wall cavities and roof voids
B. Beneath suspended floors
C. Within voids caused by settlement or subsidence
D. Drains and soakaways
Gas Characteristic Situations (CS)

Building Types
Source: BS 8485:2015
* Can have multiple types in one physical building.
| Type A | Type B | Type C | Type D | |
| Ownership | Private | Private Or Commercial/Public,
PossibleMultiple |
Commercial/ Public | Commercial/
Industrial |
| Control (Change of use, Structural alterations, Ventilation) | None | Some but not all | Full | Full |
| Room Sizes | Small | Small/ Medium | Small To Large | Large Industrial/ Retail Park Style |
Gas Protection Scoring
Source: BS 8485:2015
| Minimum Gas Protection Score (Points) | ||||
| CS | High Risk | Medium Risk | Low Risk | |
| Type A Building | Type B Building | Type C Building | Type D Building | |
| 1
2 3 4 5 6 |
0
3.5 4.5 6.5A) __B) __B) |
0
3.5 4 5.5A) 6.5A) __B) |
0
2.5 3 4.5 5.5 7.5 |
0
1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 6.5 |
A) Residential buildings should not be built on CS4 or higher sites unless the type of construction or site circumstances allow additional levels of protection to be incorporated, e.g. high-performance ventilation or pathway intervention measures, and an associated sustainable system of management of maintenance of the gas control system, e.g. in institutional and/ or fully serviced contractual situations.
B) The gas hazard is too high for this empirical method to be used to define the gas protection measures.
Common Ground Gases
Radon
Methane
- Amounts to 50% of our annual radiation dose.
- Present in all soil and rock.
- 3.3% of all deaths from lung cancer are related to radon in the home.
- A Colourless, Asphyxiating Gas.
- Can produce Carbon Monoxide.
- Forms highly flammable and potentially explosive mixtures in air, between 5% and 15%.
CarbonDioxide
Petroleum Hydrocarbon & VolatileOrganic Compound (VOC) Contamination
- Causes Drowsiness, Unconsciousness and Cardiovascular Damage.
- Classed as a ‘substance hazardous to health’ under the Control of
Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH).
- Highly flammable and explosive.
- Irritant and Asphyxiant.
- Cause short-term and long-term health effects.
Radon
- Amounts to 50% of our annual radiation dose.
- Present in all soil and rock.
- 3.3% of all deaths from lung cancer are related to radon in the home.
Methane
- A Colourless, Asphyxiating Gas.
- Can produce Carbon Monoxide.
- Forms highly flammable and potentially explosive mixtures in air, between 5% and 15%.
CarbonDioxide
- Causes Drowsiness, Unconsciousness and Cardiovascular Damage.
- Classed as a ‘substance hazardous to health’ under the Control of
Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH).
Petroleum Hydrocarbon & VolatileOrganic Compound (VOC) Contamination
- Highly flammable and explosive.
- Irritant and Asphyxiant.
- Cause short-term and long-term health effects.
